

Improvement in Safety Culture Linked to Better Patient and Staff Outcomes
Insights Report
Every day, in every hospital across America, care teams work to provide safe, high-quality care to each and every patient. Part of that work includes continually identifying what drives better outcomes, and then implementing changes to improve patient care.
AHA’s insights report series features learnings gained in collaboration with data partners to better analyze hospital and health system progress on patient safety. In September 2024, AHA partnered with Vizient to release a report showing that numerous outcome measures of health care quality and patient safety — including mortality and healthcare-associated infections — are improving while hospitals care for more patients with significant health care needs.
The latest insights report, created in collaboration with Press Ganey, highlights progress on additional outcome measures of patient safety including some that reflect the ongoing work nurses lead to protect patients. In addition, Press Ganey’s comprehensive data shows clear improvement on the experience of both patients and the health care workforce. It also shows improvements in safety culture, which is a leading indicator of better safety outcomes and better experiences for patients and staff.
Key Insights
Data in this report show that:
- Hospitals are performing at or better than pre-pandemic levels on multiple measures of quality and patient safety, including patient falls and pressure injuries (i.e., bed sores) that reflect work led by nurses to care for patients.
- Millions of patients report that their overall care experience is improving.
- Press Ganey data from more than 1 million members of the health care workforce show a rebound from pandemic lows in engagement, resilience and safety culture.
- Patient safety, patient experience, workforce experience, and well-being are all tied together by a hospital or health system’s culture of safety. Across clinical settings — the single largest driver of a patient’s reported experience of care is how well their care team members work together. Better teamwork has long been shown to drive better outcomes.
Evidence in Key Areas Show Care is Getting Safer
The Press Ganey National Database of Nursing Quality Indicators (NDNQI) dataset reflects quality measures reported by 25,652 units across 2,430 inpatient acute care hospitals. Analysis of four key measures in NDNQI data includes catheter-associated urinary tract infection (CAUTI), central lineassociated bloodstream infection (CLABSI), patient falls that result in harm, the number of patients who develop hospital-acquired pressure injuries (HAPI), also known as bed sores. The analysis shows the incidence of all measures have declined since their pandemic peaks, with nearly all measures across all units back to or better than pre-pandemic levels.
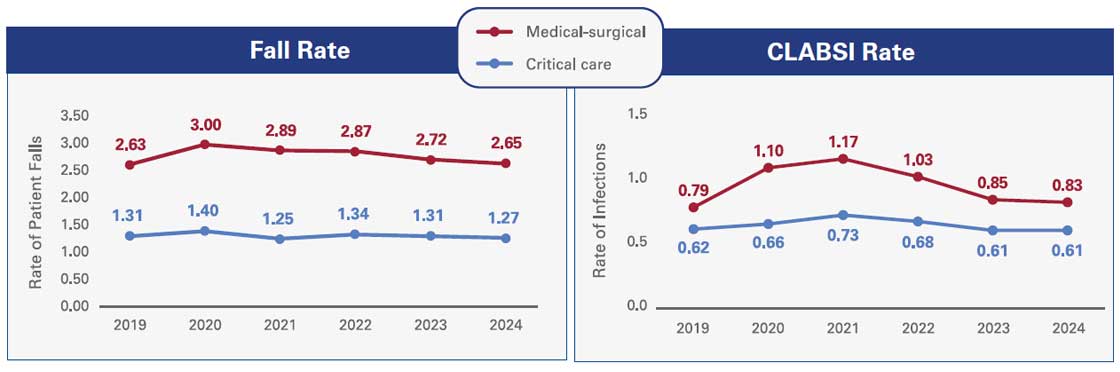
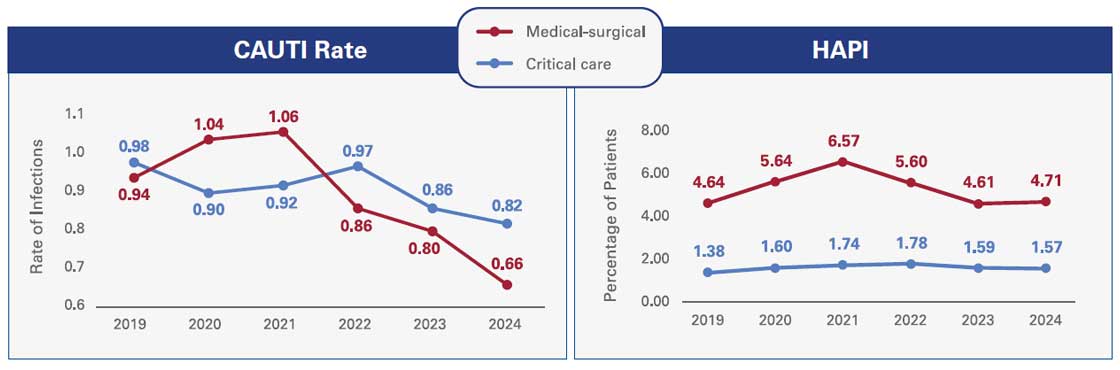
Source: ©2025 Press Ganey. All rights reserved; a PG Forsta company.
Note: Falls are measured as total patient falls per 1,000 patient days; CLASBI is measured as central line-associated bloodstream infections per 1,000 central line days; CAUTI is measured as catheter-associated urinary tract infections per 1,000 catheter days; and HAPI prevalence is measured as the percentage of surveyed patients with hospital-acquired pressure injuries.
Patients Say Their Care Experience and Perception of Safety are Improving
Press Ganey works on behalf of 75% of U.S. acute care hospitals and medical practices across the country to survey patients regarding their care experiences and gain insights into how hospitals are working to deliver safe and effective care. Included in the surveys are questions that explicitly ask patients about their perception of staff’s efforts to keep them safe, along with questions about other facets of care that contribute to greater safety, such as teamwork among staff, attention and responsiveness to patient needs, and communication between patients and members of the clinical care team. Importantly, the data for this report, based on responses from 13 million patients, show steady gains in their perceptions of both experience of care and safety of care after a drop due to the COVID-19 pandemic. Results show hospitals and health systems are on the path to returning to pre-pandemic levels of safety.
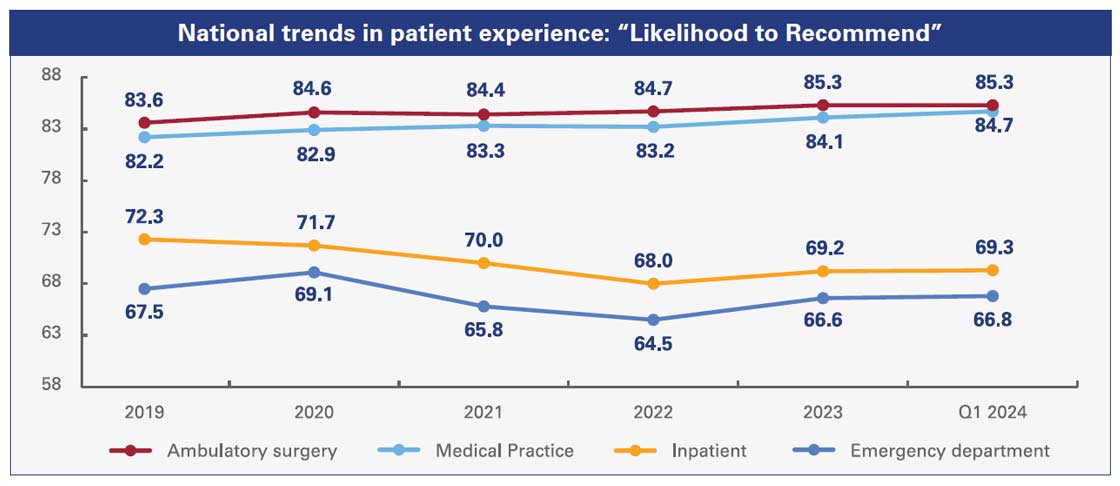
Source: ©2025 Press Ganey. All rights reserved; a PG Forsta company.
One of the key factors driving improvements in patients’ perceptions of care is the teamwork of their caregivers. Across clinical areas — inpatient and outpatient, surgical and medical, emergency and scheduled — the single largest driver of a patient’s likelihood to recommend a hospital, facility or provider is perception on how well their care team members work together. Better teamwork has long been shown to drive better outcomes.
What earns patients’ confidence and loyalty?
Patients are attuned to team dynamics and interpersonal competencies.
National analysis of key drivers of likely to recommend by setting
Emergency
- Staff worked well together
- Cared about you as a person
- Attention to your needs
- Treat with courtesy/respect
Inpatient
- Staff worked well together
- Response to concerns
- Attention to your needs
- Attitudes toward requests
Med Practice
- Staff worked well together
- Concern for questions/worries
- Explanation of condition/problem
- Include in decisions
Clinic
- Staff worked well together
- Treat with respect/dignity
- Response to concerns
- Trust skill of staff
Amb. Surgery
- Staff worked well together
- Response to concerns
- Nurses’ concern for comfort
- Provider response to concerns/questions
Urgent Care
- Staff worked well together
- Provider listened
- Explanation of condition/problem
- Include in decisions
Source: ©2025 Press Ganey. All rights reserved; a PG Forsta company.
Similarly, patients who perceive that their care was safe are 2.5 to 3 times more likely to recommend their hospital to others. Their perceptions of safety are based on their own interactions with hospital team members, their observations regarding practices such as handwashing and cleanliness, and how they see team members interacting with one another to deliver care. Specifically, when asked about their confidence in the care they received and their willingness to recommend a hospital to others, patients ranked hospitals more highly when they perceived the hospital team to be working well together and to be attentive to the patients’ needs and questions.
Workforce Experience and Well-being are Improving
At its core, health care is a uniquely human experience centered around people caring for other people. This is why hospitals and health systems pay close attention to and invest in the well-being of their workforce. An energized and engaged workforce improves the care provided to patients, the physical and psychological wellbeing of patients, and how patients perceive the work to keep them safe. As the enormous strain of the COVID-19 pandemic recedes, the health care workforce is beginning to rebound as well. Press Ganey data from 1.7 million members of the health care workforce show a rise in their reported experience and resiliency. A resilient workforce is essential in health care, given the complex and high stakes nature of the work.
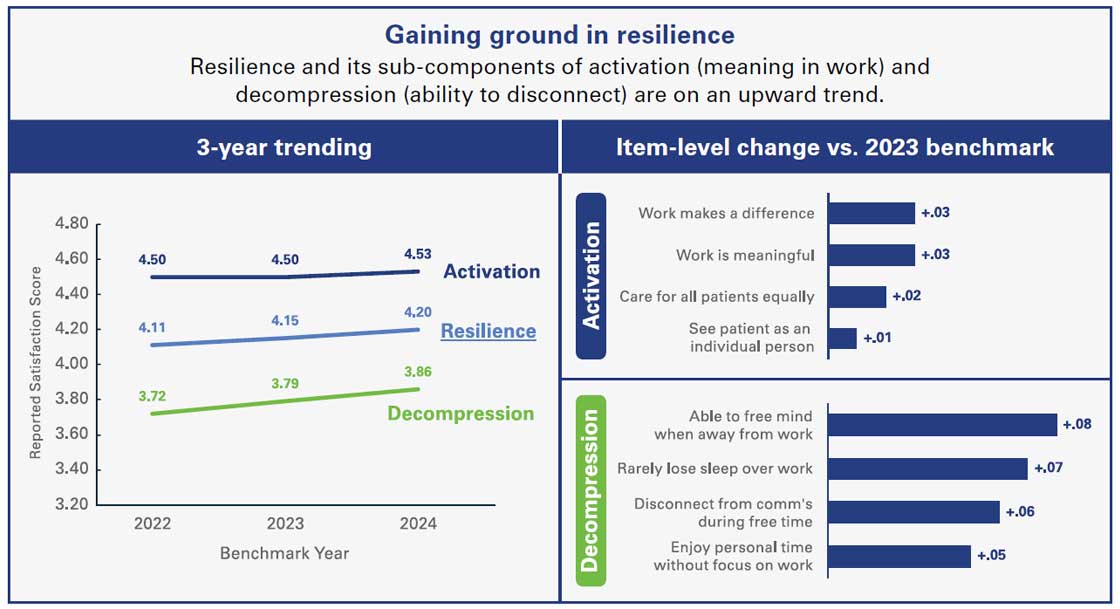
Source: ©2025 Press Ganey. All rights reserved; a PG Forsta company.
Hospitals that score higher on team member engagement surveys also see higher patient experience scores reported from patients. This correlation gets more pronounced every year, with the top performing quartile of hospitals on staff engagement in 2023 scoring in the 80th percentile on patients’ likelihood to recommend.
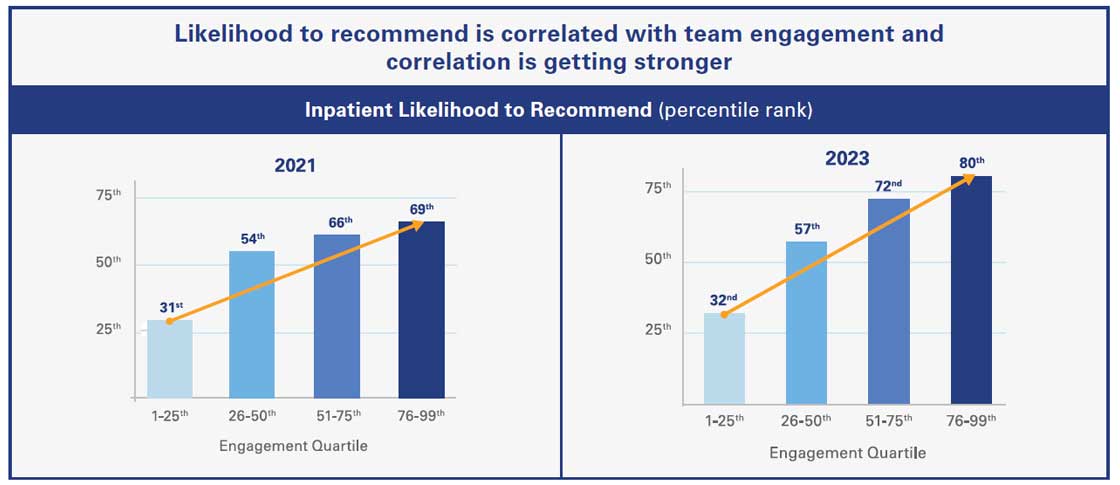
Source: ©2025 Press Ganey. All rights reserved; a PG Forsta company.
Safety Culture is Essential
A critical factor in generating both better patient outcomes and care teams’ engagement in their work is a strong safety culture. A strong safety culture supports the teams through the demanding tasks associated with care delivery and makes a noticeable difference in how patients experience their care, leading to safer care and a more resilient care delivery system.
A culture of safety is an environment in which everyone, including patients and families:
- Can speak up when they see something that might not be right.
- Is confident that improvements occur when issues are reported.
- Is dealt with fairly and compassionately when an error occurs.
- Experiences effective teamwork and communication.
An organization’s safety culture is assessed with evidence-based survey tools, such as the instrument Press Ganey developed, which gather responses from over 1 million hospital staff each year. The Press Ganey data show a positive relationship between the level of care team engagement in their work and the hospital scores for patient safety culture. When caregivers feel that they are supported, working with an effective team and doing meaningful work, they are more likely to be deeply engaged in their work.
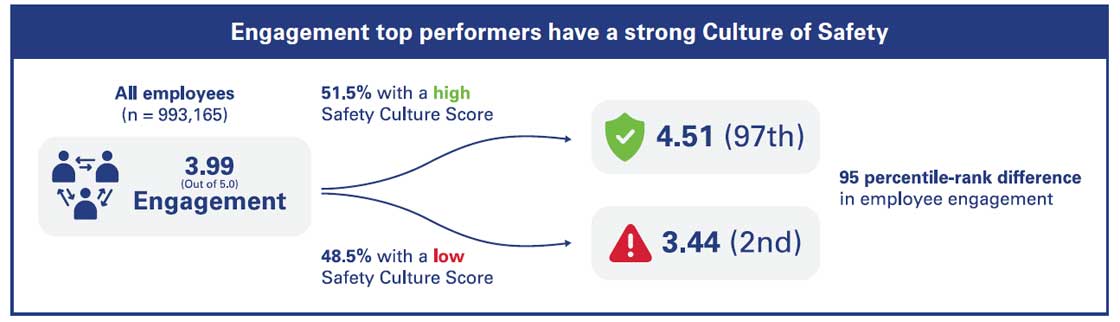
Source: ©2025 Press Ganey. All rights reserved; a PG Forsta company.
Opportunities to Enhance Safety Culture
In the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals’ performance in both safety culture and quality and safety metrics have rebounded and begun to plateau. Resources and teamwork remain areas with the greatest potential for growth. While prevention and reporting experienced an increase previously, the recent downward trend highlights the need for ongoing prioritization.
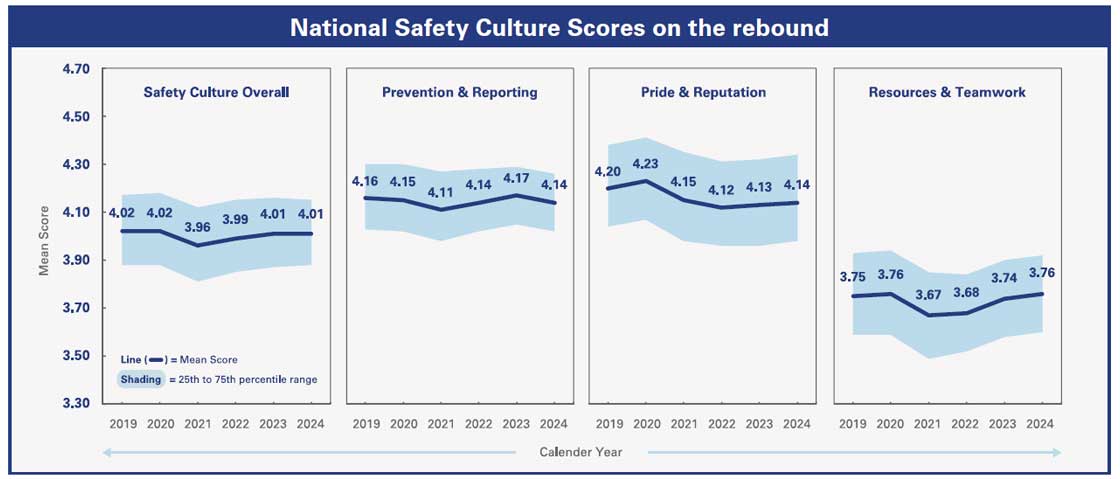
Source: ©2025 Press Ganey. All rights reserved; a PG Forsta company.
Press Ganey’s data establish how closely all of these outcomes — patient safety outcomes, patient experience, workforce engagement experience and resilience — are tied together by a hospital or health system’s culture of safety.
A Continuous Journey to Improve
Improvement is a continuous pursuit, and hospitals have been and will remain deeply committed to advancing the safety and quality of their care, the way in which patients experience care, and the wellbeing of their care teams. By improving the patient and workforce experience, identifying and addressing risks to patient or staff wellbeing, improving communications and understanding of what patients and their families value in their care experience, and implementing innovative strategies, hospitals will continue to demonstrate their commitment to patient safety.
One of the key goals of the American Hospital Association’s Patient Safety Initiative is to help hospitals and health systems improve the culture of safety. Launched in 2023, AHA’s Patient Safety Initiative catalyzes hospitals’ and health systems’ collective expertise and momentum for improvement and focuses on 1) safety culture, 2) identifying and addressing disparities in health care outcomes, and 3) the wellbeing of the workforce.
Through the work of the Patient Safety Initiative, hospitals and health systems are using safety improvement strategies that have a history of success, as well as trying new and innovative approaches to further enhance their work.
To help leaders and boards learn from their counterparts in other hospitals and health systems, AHA has produced the Leading for Safety video series hosted by former Chair of the AHA Board of Trustees Mindy Estes, M.D., and featuring leaders from hospitals and health systems that have been recipients of AHA’s Quest for Quality award. The AHA’s Safety Speaks podcast series also features many quality and safety leaders talking about their innovative approaches to safety.

